Healthcare cybersecurity is the practice of protecting electronic patient data from unauthorized access or theft. It is a growing concern for healthcare organizations as the use of electronic health records (EHRs) and other health information technologies (HITs) increases.
The healthcare industry is particularly vulnerable to cyber attacks due to the sensitive nature of the data it collects and stores. This data includes patients’ personal information, medical records, and financial information. A breach of this data can have serious consequences for patients, healthcare organizations, and the overall healthcare system.
That’s why it’s so important for healthcare providers and organizations to have strong cybersecurity measures in place. This complete guide from Oppos cybersecurity experts in Canada will help you understand the threats to healthcare cybersecurity and what you can do to protect your organization.

Threats to Healthcare Cybersecurity
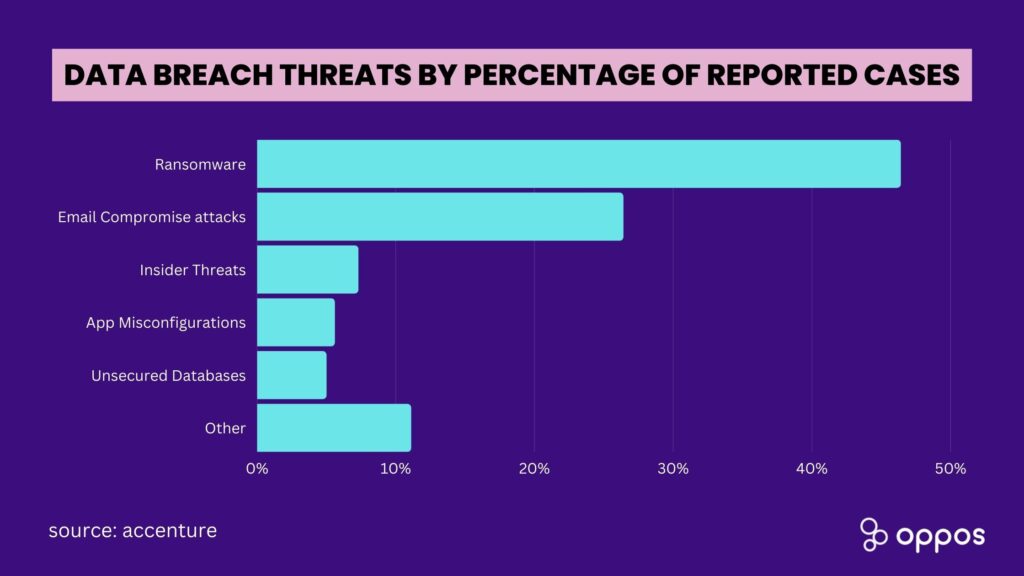
Various cyberattacks pose significant risks to patient care and the healthcare industry. Healthcare providers face challenges from denial of service, ransomware, phishing, and malware attacks. These threats impact healthcare providers and jeopardize the safety and privacy of patients’ sensitive data.Types of cyberattacks in the healthcare sector
There are a variety of cyberattacks that can target the healthcare sector. These attacks can range from simple viruses that disrupt healthcare operations to more sophisticated attacks that aim to steal protected health information (PHI).
Some of the most common types of cyberattacks in the healthcare sector include:
- Denial of service (DoS) attacks: These attacks aim to disrupt healthcare operations by flooding healthcare facilities with requests, making it difficult for legitimate users to access system resources.
- Ransomware attacks: These attacks aim to encrypt healthcare data and demand a ransom from the healthcare organization in order to decrypt the data.
- Phishing attacks: These attacks use email or other communication channels to trick healthcare employees into revealing PHI or other sensitive information.
- Malware attacks: These attacks involve malicious software that can damage healthcare systems or steal PHI.
Impact of Cyberattacks on Healthcare Organizations
Cyberattacks can lead to financial loss, business loss, and increased costs for healthcare providers, including those associated with cybersecurity technology, expertise, insurance premiums, and public relations support. They can also result in operational disruption, altering business practices, and reputational damage. Healthcare providers may be forced to rethink how they collect, store, and secure sensitive information. The reputational damage from cyberattacks can lead to reduced trust from patients and suppliers and a potential drop in market value. Furthermore, healthcare organizations face potential revenue loss as customers seek more secure providers or hackers extort victims. The theft of valuable intellectual property, including medical systems and medical data, can also significantly impact healthcare providers. Protecting patient records, health and human services, and the integrity of medical equipment helps preserve the healthcare industry’s reputation in the face of growing cyber threats.Cost of Cyberattacks on Healthcare
Cyberattacks on healthcare systems are becoming more common and more costly. A recent study found that the average cost of a data breach for a healthcare organization is now $10 million. This is a dramatic increase from the roughly $4 million average cost just two years ago.
With the cost of cyberattacks on the rise, it’s more important than ever for healthcare organizations to invest in robust security measures. By implementing strong security protocols, healthcare organizations can protect their patients’ data and minimize the risk of a costly data breach.
What's your Cybersecurity Grade?
Essential Elements of a Healthcare Cybersecurity Program
The essential elements of a healthcare cybersecurity program aim to protect patient care, patient data, and healthcare industry assets from cyber threats. Key elements include cybersecurity policies and procedures, training and awareness programs, risk assessments, strong access controls, encryption, vendor management, incident response plans, and continuous monitoring. Implementing these measures helps safeguard medical systems, equipment, and connected medical devices, ensuring patient information is safe and the integrity of health and human services while mitigating healthcare cybersecurity threats.Cybersecurity policies and procedures
A cybersecurity policy is a formal document that outlines an organization’s rules and procedures for managing its digital security. A good cybersecurity policy should address all aspects of an organization’s security, from employee access control to data encryption and device security. An effective cybersecurity policy will help an organization to protect its data and systems from attack, and it can also serve as a valuable tool for raising awareness about security risks and best practices among employees.
Cybersecurity procedures are documents that provide step by step instructions on how to perform a specific task. There are many cybersecurity procedures that businesses can implement to help protect their data and networks from attacks. Some common procedures include installing and updating antivirus software, enforcing strong passwords, and encrypting sensitive data. While policies outline the direction of a business’s cybersecurity operations, the procedures documents explain exactly how certain tasks should be performed.
Cybersecurity training and awareness programs
As the threat of cyberattacks continues to grow, it’s critical for companies to have cybersecurity training and awareness programs in place. These programs help employees learn how to identify and avoid potential security threats, and they can be extremely effective in protecting your business from a cyberattack.
However, many companies still don’t have these programs in place. If you’re one of them, now is the time to take action. Implementing a cybersecurity training and awareness program can help you mitigate the risk of a cyberattack and keep your business safe.
Risk assessments and vulnerability scans
As part of a commitment to information security, your organization should regularly perform risk assessments and vulnerability scans. Risk assessments help you identify where your organization is vulnerable to attack, and vulnerability scans help you find the specific weaknesses that could be exploited.
Risk assessments and vulnerability scans are an essential part of any organization’s security strategy. These should be done at least once per year as part of your organization’s overall cybersecurity strategy. By taking the time to perform these scans regularly, you can help protect your organization from potential attacks.
Implementing strong access controls
When it comes to information security, one of the most important tools you have at your disposal is access control. Access control is the process of restricting access to systems, data, and other resources. By implementing strong access controls, you can help to keep your company’s information safe and secure.
There are many different ways to implement access control, but one of the most effective is the principle of least privilege. This principle dictates that users should only have the bare minimum amount of access needed to perform their job duties. By granting only the necessary level of access, you can help to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
In order to implement the principle of least privilege, you’ll need to carefully assess each user’s needs and then assign the appropriate level of access. This can be a time-consuming process, but it’s essential to ensuring the security of your company’s assets.
Encryption for Data Protection
Encryption is a process of transforming readable data into an unreadable format. This is done using a key, which is a piece of information that controls the mathematical algorithm used in the encryption process. The encryption process makes it very difficult for anyone to access the data without the key. This means that organizations can encrypt data that is stored (at rest) or data being sent to another destination (in transit) and this offers a high level of assurance that the data will not be read by anyone other than the intended recipient.
There are two main types of encryption: symmetric and asymmetric. Symmetric encryption uses the same key for both the encryption and decryption process. Asymmetric encryption uses two different keys, one for encryption and one for decryption. Symmetric encryption has the benefit of being faster to use while asymmetric is generally considered more secure.
Vendor Management
In cybersecurity, vendor management is the process of identifying, assessing, and monitoring external vendors that provide services or products that impact the security of an organization. This includes vendors that provide software, hardware, or cloud-based solutions.
Vendor management is important in cybersecurity because it helps to ensure that vendors are meeting their obligations and that their products or services are not introducing new risks to the organization. By assessing and monitoring vendors, organizations can make sure that they are using vendors that are trustworthy and that their products or services are effective.
Incident response plans
An incident response plan (IRP) is a formalized process for dealing with a network security incident. It is a crucial part of an organization’s security posture, as it provides a structured approach for dealing with incidents in a timely and effective manner.
The incident response process typically consists of four main stages: preparation, detection and analysis, containment and eradication, and recovery. Each stage is important in its own right and must be carefully planned and executed in order to be effective.
An incident response plan is only as good as its ability to be executed in a real-world scenario. Therefore, it is important to regularly test and update the IRP in order to ensure that it is ready to be used in the event of a security incident.
Continuous Monitoring
As the title suggests, continuous monitoring is the practice of monitoring data and systems on a continual basis. By doing so, organizations can identify potential security issues early on and take steps to mitigate them. Continuous monitoring is an important part of any security program and can help you keep your data and systems safe from potential threats.
Regulatory Framework for Healthcare Cybersecurity
The regulatory frameworks for healthcare cybersecurity encompass guidelines and standards to ensure patient care, protect patient data, and maintain the integrity of healthcare systems. Key regulatory frameworks include PIPEDA, PHIPA, and provincial and territorial privacy commissioners. These frameworks guide chief information security officers, medical device companies, and healthcare providers in implementing cybersecurity solutions for clinical decision support systems, operating systems, and connected devices. Adherence to these industry regulations helps safeguard patient information and promotes a secure healthcare environment.PIPEDA
The Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA) is a federal law that applies to organizations that collect, use or disclose personal information in the course of commercial activity.
PIPEDA sets out the ground rules for how organizations must handle personal information in a fair and responsible manner. It also gives individuals the right to access and correct their personal information held by organizations.
Organizations that are subject to PIPEDA must comply with its provisions, unless they are exempt under the Act. Exemptions may apply in certain circumstances, such as for national security, law enforcement or investigations.
PIPEDA is administered by the Office of the Privacy Commissioner of Canada (OPC). The OPC is responsible for ensuring that organizations comply with the Act and investigate complaints from individuals about possible breaches of the law.
PHIPA
The Personal Health Information Protection Act (PHIPA) is a provincial law that protects the privacy of an individual’s personal health information. The law applies to all organizations that collect, use or disclose personal health information in the course of providing health care or administering health care benefits.
Under PHIPA, personal health information includes any information about an individual’s physical or mental health, including information about his or her health history, genetic makeup, and any care or treatment that he or she has received.
PHIPA sets out rules for how personal health information must be collected, used and disclosed by organizations covered by the Act. It also gives individuals the right to access their own personal health information and to correct any inaccuracies in that information.
Provincial and territorial privacy commissioner
The provincial and territorial privacy commissioner is responsible for protecting the privacy of individuals with respect to the collection, use and disclosure of their personal information. The commissioner also has the mandate to investigate complaints and to make recommendations to improve the privacy practices of organizations. The provincial and territorial privacy commissioner is independent from the provincial or territorial government and reports directly to the legislature.
Healthcare Cybersecurity Best Practices
Patient data protection has become a critical concern for healthcare systems, medical device companies, and medical services. By implementing these best practices, organizations can ensure the robust protection of patient data.Conduct Regular Risk Assessments
It’s important for businesses to conduct regular cyber risk assessments in order to identify potential hazards and mitigate risks. By taking a proactive approach to risk management, businesses can protect themselves from potential liabilities and losses.
Once you’ve identified the risks, you can develop a plan to mitigate them. This may involve implementing new safety procedures, investing in insurance, or taking other measures to protect your business.
Implement Strong Access Controls
When it comes to security, one of the most important things you can do is to implement strong access controls. This means restricting access to sensitive data and systems to only those who need it. By doing so, you can greatly reduce the risk of unauthorized access and data leaks.
There are a few different ways to implement strong access controls. One is to use role-based access control, which allows you to restrict access based on a person’s job function. Another is to use least privilege, which means only giving users the bare minimum amount of access they need to do their job. And finally, you can use access control lists, which allow you to specifically allow or deny remote access to specific resources.
No matter which method you choose, strong access controls are essential to keeping your data safe.
Regularly Update and Patch Systems
It is important to regularly update and patch systems in order to fix known vulnerabilities and keep your system secure. Cyber criminals are constantly searching for new vulnerabilities to exploit, so it is important to keep your system up-to-date to protect it from attack.
There are two main types of updates: security updates and general updates. Security updates address vulnerabilities that have been discovered and are a high priority for patching. General updates include new features and improvements and are not as critical for security purposes.
Implement Encryption
One of the most important things you can do to secure your data is to implement encryption. Encryption is a process of transforming readable data into an unreadable format, which makes it much more difficult for unauthorized individuals to access your information. There are a variety of encryption methods available, and the best method for you will depend on your specific needs.
Conduct Regular Security Awareness Training
As a business owner, it’s important to ensure that your employees are properly trained on security protocol and procedure. Security awareness training should be conducted on a regular basis – at least once per quarter – to ensure that your employees are up-to-date on the latest security threats and how to protect your business from them.
There are a number of ways you can conduct security awareness training, from in-person sessions to online courses. Whichever method you choose, make sure that your employees are engaged and able to ask questions. You can even consider using gamification to make the training more fun and interactive.
By conducting regular security awareness training, you can help to protect your business from costly security breaches.
Develop an Incident Response Plan
An incident response plan (IRP) is a formal document that outlines the steps a company will take in the event of a security incident. The goal of an IRP is to help a company minimize the damage caused by an incident and to get back to business as quickly as possible. Developing an IRP should be a collaborative effort that involves input from all levels of the organization. The goal is to create a plan that is comprehensive and tailored to your organization’s specific needs.
Conduct Regular Security Audits
As a business owner, it’s important to make security a priority. One way to do this is to conduct regular security audits. A security audit is a thorough assessment of your company’s security posture. It can help you identify weaknesses in your security system and take steps to correct them.
There are many different types of security audits, but they all share a common goal: to improve your security. By conducting regular security audits, you can ensure that your company is doing everything it can to protect itself from potential threats.
Utilize Multi-Factor Authentication
There’s no denying that password security is important. But with the release of new and improved authentication methods, it’s time to start utilizing multi-factor authentication (MFA) to further secure your online accounts. Multi-factor authentication is a process that requires more than one method of verification before granting access to an account. This could include something you know (like a password), something you have (like a physical token), or something you are (like a fingerprint). Using multi-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security to your accounts.
Get Your Health System Secure with Oppos!
In conclusion, cybersecurity in the healthcare industry is a complex and ever-evolving issue. There are many steps that organizations can take to improve their cybersecurity posture, but it is an ongoing battle. This guide provided an overview of the healthcare cybersecurity landscape and some tips on how to improve cybersecurity in the health sector. For more tips and tricks, subscribe to our newsletter and reach out to us for help with your organization’s cybersecurity operations.
Don’t let your health systems fall victim to cyberattacks! Secure your patients’ data and ensure the integrity of your systems with Oppos Inc. We specialize in cybersecurity training for healthcare practitioners and penetration testing to safeguard your most sensitive information. Our expert team will empower your staff with the knowledge and skills to combat threats and protect your reputation. Act now – reach out to Oppos for risk assessment!
Don't wait – secure your data and boost patient's confidence with Oppos' ISO healthcare assessments.
Healthcare Cybersecurity FAQs
Cyber security is crucial for medical equipment to protect patient safety, data privacy, and ensure functionality. Strong security measures mitigate risks from cyber supply chain attacks and uphold compliance with security rules. Safeguarding medical devices is essential for maintaining trust and providing reliable healthcare services.
To protect connected medical devices from cyberattacks, keep operating systems updated, implement strict privacy and security policies, and adhere to security rules. As more connected medical devices emerge, healthcare professionals must prioritize securing private patient data and establishing robust defense mechanisms to maintain trust and patient safety.
Medical device security challenges include adhering to security rules, navigating complex cybersecurity landscapes, and complying with healthcare laws. Medical professionals must balance protecting health data and patient outcomes while following industry-led guidelines. Ensuring robust security measures requires constant vigilance and adapting to evolving threats to medical device hijacking.
Medical devices with known vulnerabilities often include legacy systems, outdated computer systems, and devices lacking regular updates. These vulnerabilities expose health systems to enterprise risk and sensitive patient information to breaches. Health practitioners and other C-suite executives must prioritize cybersecurity software and device updates to critical systems.