As a business owner or decision-maker, you are responsible for the security of your company’s data and systems. In today’s threat landscape, that includes protecting against cyberattacks.
While there are many different types of risks that businesses need to monitor, there are five cybersecurity key risk indicators (KRIs) that are particularly important. These KRIs will give you a better understanding of your organization’s current cybersecurity posture and help you identify areas that need improvement.
So what are these five KRIs? Read on to find out!

What are Key Risk Indicators for Cyber Security?
Key risk indicators (KRIs) metrics help assess an organization’s risk level and track the evolution of its risk profile. By analyzing threats and vulnerabilities reported by security tools, cybersecurity operations can gain valuable insights into the organization’s exposure to potential attacks.
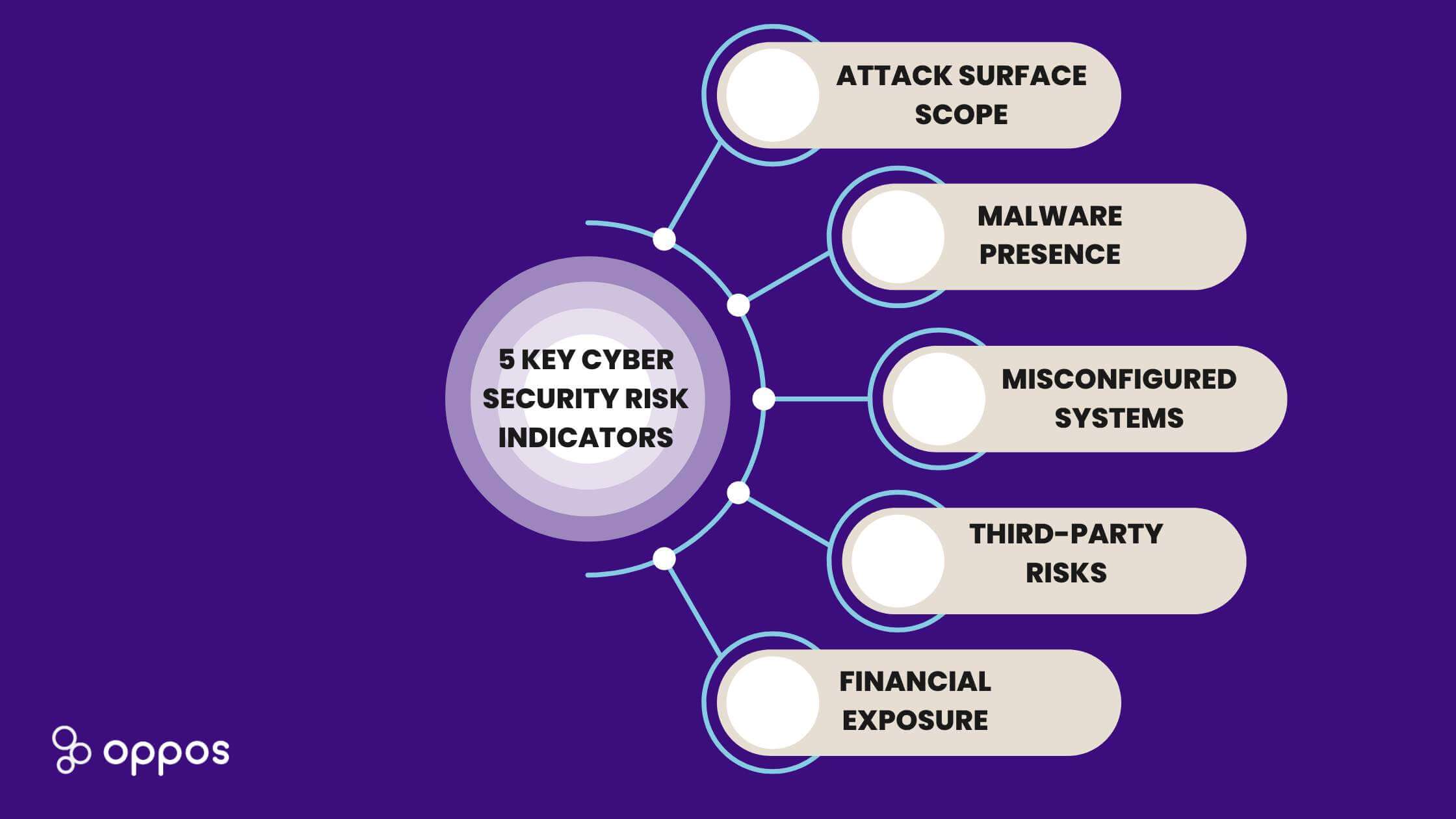
5 Key Cyber Security Risk Indicators
Attack Surface Scope
Organizations should adopt a systematic and thoughtful approach to reducing their attack surface. By identifying and addressing vulnerabilities, they can make it more difficult for attackers to succeed.
When scoping the attack surface, organizations should consider both external and internal systems and components. External systems are those that are publicly accessible, while internal systems are only accessible to authorized users. Each type of system has its own set of risks that need to be considered.
Organizations should also keep in mind that the attack surface is constantly changing. As new systems and components are added, the attack surface grows. Similarly, as old systems are retired or removed, the attack surface shrinks. It’s important for organizations to regularly review their attack surface and make sure they are doing everything they can to keep it as small as possible.
Malware Presence
The prevalence of malware on your systems is a good indicator of risk for your organization. Malware is a growing problem for companies of all sizes. Malware is a type of software that is designed to damage or disable computer systems. It can be spread via email, websites, and even through social media. Malware can lead to data loss, financial damage, and even reputation damage for a company.
No matter how robust your cybersecurity program is you will find malware on your systems from time to time. But the frequency of this and how dangerous the malware is can help you determine how at risk you are. For example an occasional occurrence of adware is very different from several instances of ransomware.
The best way to protect your company from malware is to be aware of the threat and to take steps to prevent it. This includes having a good anti-malware solution in place, consistent monitoring of your environment as well as educating your employees about the potential of cyber threats and how to deal with them.
Misconfigured Systems
Systems must be configured correctly to maintain security and prevent data breaches. Secure configuration simply means adjusting the settings of your machines to achieve the most secure state possible while not interfering with their business function. To do this it’s best to use a secure configuration guide, such as those provided by the Center for Internet Security (CIS). Unfortunately, many systems are misconfigured, which can leave them open to attack.
Third-Party Risks
As the world becomes increasingly digital, the risks associated with cyberattacks are also on the rise. While many companies are aware of the dangers of cyberattacks, they may not be as aware of the risks posed by third-party vendors.
Third-party vendors are organizations that provide goods or services to other companies. They can be anything from suppliers to software providers. While they are not part of a company, they still have access to the company’s data and systems. This makes them a potential weak spot that hackers can exploit. This is why it’s important for companies to take steps to reduce the risks posed by third-party vendors. Such as performing due diligence when selecting vendors, having security measures in place to protect their data and systems, and regularly monitoring the vendors’ compliance with these measures.
Financial Exposure
When it comes to cyber attacks, businesses face a variety of potential financial exposures. These can include the cost of recovery from the attack, loss of revenue due to downtime, loss of customer confidence, and reputational damage. In some cases, cyber attacks can also lead to regulatory penalties and legal liabilities.
To manage these financial exposures, businesses need to have an effective cyber security strategy in place. This should include measures to prevent and detect attacks, as well as plans for responding quickly and efficiently in the event of an attack. By taking these steps, businesses can minimize the financial impact of a cyber attack and protect their bottom line.
How is Cybersecurity Risk Measured?
Cybersecurity risk is the chance of disruption or unauthorized access to systems, networks, or data due to a security breach. This risk can be measured in several ways, including the likelihood of an attack, the impact of an attack, and the cost of an attack.
The first step in measuring cybersecurity risk is to identify the potential threats to your systems. Once you know what threats exist, you can then assess the likelihood of those threats being realized. This can be done through a variety of methods, including vulnerability assessments, threat modeling, and security audits.
Once you have a good understanding of the potential risks and the likelihood of the attack then you can then begin to quantify the impact of those risks. This includes estimating the cost of an attack, the downtime caused by an attack, and the damage to your reputation that could result from an attack. The final formula will look something like this:
Risk = Cost X likelihood of an attack
Used in an example, if we believe that a ransomware attack would cost the company $1 million and we believe that there is a 10% chance of a ransomware attack happening every year then we quantify that as roughly a $100,000 cost per year.
100,000 = 1,000,000 X 0.10
How to Minimize Cybersecurity Risks
Cybersecurity risks have become increasingly prevalent in today’s digital landscape, posing significant threats to individuals and organizations. To mitigate these risks, it is essential to implement effective cybersecurity measures.
Develop and Implement Policies
No company is immune to cybersecurity threats, and all businesses need to have policies and procedures in place to protect themselves. While there are many different types of cybersecurity threats, there are several attacks that are more commonly used than others including viruses and malware, phishing attacks, and Denial of Service (DoS) attacks. Knowing this it’s important to have policies in place to govern how your business should respond in any of these situations.
Developing and implementing policies for cybersecurity can help to protect your company from these threats. Some of the steps you can take to develop and implement these policies include:
- Identifying and assessing cybersecurity risks
- Developing a plan to address risks
- Training employees on cybersecurity policies and procedures
- Monitoring and reviewing policies on a regular basis
By taking these steps, you can help to ensure that your company is better protected against cybersecurity threats.
Define Employee Permissions
An employee’s permissions are the limitations placed on what they can and cannot do within a company’s digital ecosystem. This usually includes things like what software they can access, what files they can edit, and what websites they can visit. By setting up proper employee permissions, a company can help protect its data and keep its workers productive.
When defining employee permissions the goal is to implement a principle of least privilege. This simply means you want to limit an employee’s permission to the minimum needed for them to properly perform their job. Secondly, you want to avoid granting access on an individual basis and instead used role-based access control (RBAC). This makes it much easier to keep track of what access the user has. Lastly, you want to ensure that review and update your employee’s permissions regularly.
Keep All Software and Hardware Up-to-Date
One of the most important things you can do to keep your computer system secure is to ensure that all software and hardware is kept up-to-date. This includes the operating system, web browsers, email clients, plugins, and any other applications you have installed. By keeping everything up-to-date, you can help reduce the chances of being attacked by malware or other security vulnerabilities.
In addition to keeping your software up-to-date, you should also keep your hardware up-to-date. This includes ensuring that your computer’s BIOS is up-to-date, as well as any firmware installed on other devices (such as routers). By keeping your hardware up-to-date, you can help minimize the chances of being affected by hardware-based security vulnerabilities.
Manage Your Third-Party Risk
Third-party risk is a growing concern for companies of all sizes. As businesses increasingly rely on outside vendors and service providers, they are also exposed to a range of new risks. These risks can come from a variety of sources, such as cyber-attacks, data breaches, and financial fraud.
If not properly managed, third-party risk can lead to serious consequences for businesses, including financial losses, reputational damage, and regulatory sanctions. That’s why companies need to have a robust third-party risk management program in place.
There are several key steps that businesses should take to effectively manage their third-party risk. First, it’s important to conduct due diligence on third parties. This means understanding their business process and their security controls, ensuring they are a legitimate business and checking their history related to data breaches and hackers. You want to make sure the company you are trusting with your data can protect it.
Next, establish clear contractual terms. You need to get your third parties to sign off on understanding your business’s expectations around data security and privacy and get them to agree to handle the data correctly.
Lastly, you should monitor third-party performance on an ongoing basis. This can be done manually or using security tools like security scorecard to monitor your third-party vendors.
Cybersecurity Requirements: Ultimate Guide to Cybersecurity Planning for Your Business
Importance of Cybersecurity Risk Management
As the world increasingly moves online, the importance of cybersecurity grows exponentially. At its most basic, cybersecurity risk management is the process of identifying, assessing, and responding to risks posed by digital threats. But in today’s landscape, that process has become much more complex.
With the vast array of digital devices and platforms in use today, there are more potential entry points for cyberattacks than ever before. And as we continue to rely more and more on technology, the stakes are getting higher. A successful cyberattack can result in the loss of sensitive data, financial damage, and even physical harm.
That’s why it’s more important than ever for businesses to have a robust cybersecurity risk management strategy in place. By taking steps to identify and assess the risks posed by digital threats, businesses can protect themselves from the potentially devastating consequences of a cyberattack.
Conclusion
As cyber threats continue to evolve, it’s important for businesses to stay up-to-date on the latest cybersecurity risks. Monitoring key risk indicators is one way to do this.
If you’re concerned about your business’s cybersecurity, consider taking advantage of Oppos Inc’s cybersecurity compliance service. Our experts can help ensure that your organization meets regulatory compliance requirements and stays protected against the latest cyber threats. Don’t wait until it’s too late; contact us today to learn more about our services
To get more tips on how to protect your business from cyber threats, subscribe to our newsletter.
Stay protected with Oppos' advanced cybersecurity solutions today!
Cybersecurity Key Risk Indicators FAQs
Creating a risk management plan begins with identifying your company key assets that need protection, identifying the threats to those assets and then planning and implementing countermeasures to those threats.
A risk assessment is an evaluation of potential risks to the company. It evaluates what the risk is, it’s potential to cause harm and how likely it is to occur.
IoT devices pose a risk because many of them have built in security vulnerabilities and often go unpatched for various reasons.
An inherent risk is a standard risk related to doing business. You can’t complete eliminate this type of risk but you can mitigate the damage from it.
The most common types of cyber risks are:
- Adware
- Ransomware
- Phishing
- Web Applications Attacks
- Privilege Escalation Attacks